
Hackmanite Gemstone: Properties, Meanings, Value & More
 Hackmanite is a variety of sodalite that is usually pink to violet in color. This gemstone has some fascinating optical properties including glowing in the dark and temporarily changing color in the sun.
Hackmanite is a variety of sodalite that is usually pink to violet in color. This gemstone has some fascinating optical properties including glowing in the dark and temporarily changing color in the sun.
Is hackmanite natural? Yep! This gem is a natural stone beloved by mineral collectors. It’s often heralded as a “natural glow-in-the-dark material.”
Is hackmanite rare? As a mineral, no. But gem-quality hackmanite stones are rare, especially transparent crystals.
Ready to learn more? Come along as we unpack what hackmanite is, its many mesmerizing properties, how much it costs, and more.
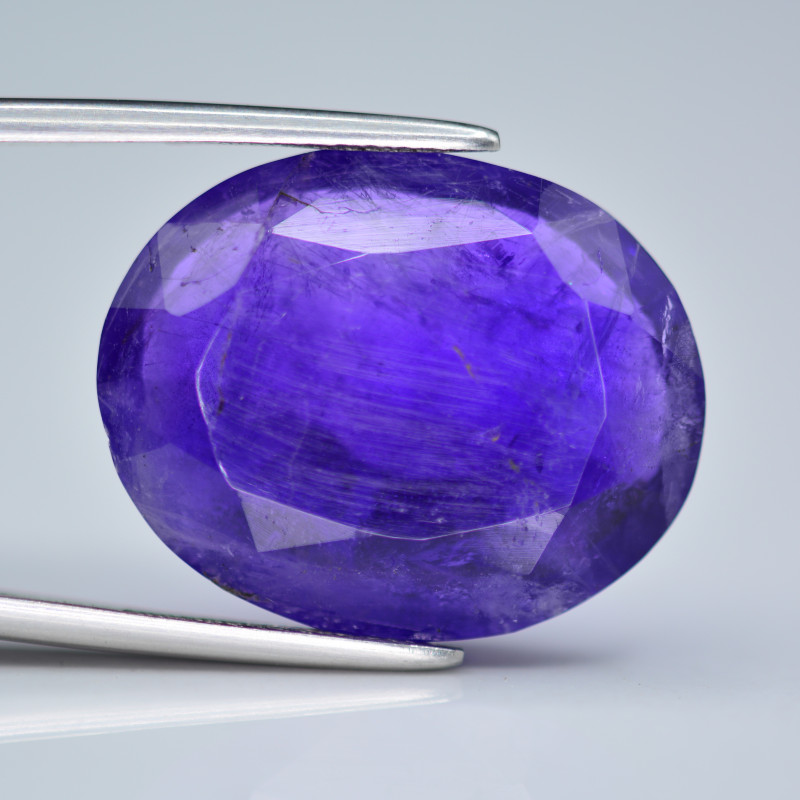

About Hackmanite Stone
Hackmanite is a semi-precious gemstone often found in a pale pink to violet color. It’s best known for its tenebrescence, which we’ll cover more in a bit.
As a zodiac stone, hackmanite benefits those born under Sagittarius or Scorpio. It’s also a planetary star stone for Neptune, making it beneficial to the Neptune-ruled Pisces.
The gem is not a traditional birthstone, but it can substitute for amethyst as a February birthstone or lapis lazuli as a September birthstone.
Hackmanite Specifications & Characteristics
Hackmanite is a variety of the mineral sodalite, along with lazurite and hauyne. Sodalite is a sodium aluminosilicate containing chloride that’s known for its rich blue-to-violet coloring.
Among the sodalite minerals, hackmanite is the tenebrescent, sulfur-containing variety, though some specimens may not have enough sulfur to be detected with X-ray analysis. However, the sulfur is what gives hackmanite its tenebrescence.
The mineral forms as masses as well as octahedral or cubic crystals. Its tenacity or toughness (resistance to breaking or chipping) is poor.
Here is a list of hackmanite’s properties:
Mohs hardness: 5.5 to 6
Color: White, blue, gray, purple, violet-blue, pink; Usually pink to violet and temporarily fades to greenish-white or gray in sunlight; Faded specimens can also be white, pink, blue, green, or red
Crystal structure: Isometric (cubic)
Luster: Vitreous or greasy
Transparency: Transparent to opaque
Refractive index: 1.479-1.487
Density: 2.14-2.40
Cleavage: Uneven or conchoidal
Fracture: Poor, 1-direction
Streak: White
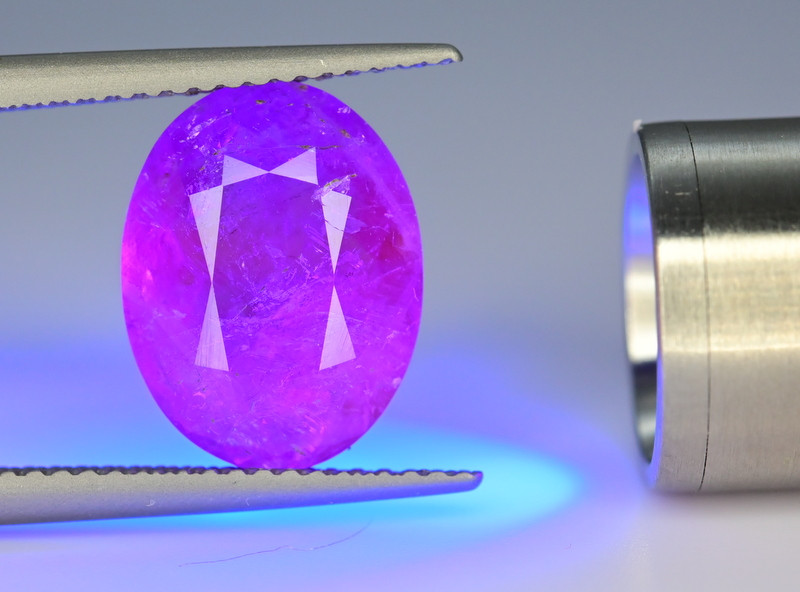
Luminescence: Usually strong fluorescence & phosphorescence, strongest under LW-UV – orange to yellow-orange in LW-UV & orange-yellow, bluish-white, or orange in SW-UV; Bright red-orange cathodoluminescence
Pleochroism: None
Dispersion: 0.018 (moderate)
Next, we’ll elaborate on some of the properties listed above — namely, hackmanite’s various types of luminescence and color-changing abilities.

Hackmanite’s Optical Properties
Although hackmanite is a pretty stone on its own, it’s most famous for its various optical properties.
The first and arguably most important property that hackmanite displays is tenebrescence, which is also called “reversible photochromism.” Of all the various types of optical phenomenon seen in gemstones, from the “cat’s eye” effect to aventurescence, tenebrescence is the rarest kind.
Tenebrescence (Color Change)
In mineralogy, photochromism describes a mineral’s ability to change color after being exposed to certain types of light, usually UV light like sunlight.
Stones with reversible photochromism (tenebrescence) can revert back to their original color, but gems with permanent photochromism cannot revert back naturally. Another example of a tenebrescent gem is scapolite, while an example of a gem with permanent photochromism is the spodumene variety called kunzite.
If you’re curious, the word “tenebrescence” comes from the Latin tenebrae, meaning “darkness” or “shadows.”
So, does hackmanite change color? Yes, hackmanite can change color under sunlight and other UV light, though this can take minutes to hours of exposure. Most often, pink to violet hackmanite will “bleach” under sunlight to become gray or greenish-white. Other times, light purple hackmanite can turn saturated purple under sunlight.
Plus, hackmanite can change color over and over without its original color wearing down or fading.
It’s important to note that this is a different phenomenon than the one seen in color-changing gems like alexandrite.
Besides changing color, you’ll also see hackmanite glow under various conditions. But why does hackmanite glow? It all comes down to its luminescence.

Luminescence
The term “luminescence” refers to a substance (like a mineral) emitting light without being heated. There are multiple types of luminescence, and they differ by what type of energy causes the light emission.
Some important types of luminescence to know are:
Photoluminescence: Luminescence from the substance absorbing photons (energy from light, like sunlight) that excites electrons; In other words, the glow is triggered by external light
Fluorescence: Type of photoluminescence where the light emitted is a different wavelength than the light absorbed (meaning the light that triggered the luminescence); The glow is immediate but short-lived, stopping once removed from the light source
Phosphorescence: Also called persistent luminescence; Type of photoluminescence similar to fluorescence, but the glow lasts longer and continues after the material is removed from the light source; The glow’s duration can vary from seconds to hours; This is what causes “glow-in-the-dark” objects
Cathodoluminescence: Luminescence caused by the material being bombarded with electrons
Impressively, hackmanite can display fluorescence, phosphorescence, and cathodoluminescence.
Starting with fluorescence, hackmanite shows stronger, more consistent fluorescence under long-wave ultraviolet (LW-UV) light.
Hackmanite’s fluorescence under short-wave ultraviolet (SW-UV) light is weaker and varies more, possibly due to the stone’s tenebrescence. The brightness can also vary based on the stone’s source.
Hackmanite can also display the glow-in-the-dark phosphorescence, but you won’t see this in every hackmanite specimen. The hackmanite stones that do glow in the dark can glow brightly for 6 to 10 hours!
Like fluorescence, hackmanite’s phosphorescence can vary based on its source. Specimens from Afghanistan are known for having the brightest glow-in-the-dark properties.
Lastly, hackmanite emits a bright red-orange cathodoluminescence.
Alright, that’s enough science for now. Let’s take a break by looking at hackmanite’s symbolism.

Hackmanite Meaning & History
Much of hackmanite’s spiritual meaning ties back to its physical traits. The common purple coloring symbolizes spiritual growth and imagination, while other hackmanite’s blue coloring symbolizes freedom, loyalty, and stability.
The stone’s color-changing ability also reflects how our talents are often hidden until someone sparks that inner light within us.
Hackmanite can also represent balance, freedom, and celestial knowledge.
History
The name “hackmanite” doesn’t come from anything regarding technology or hacking. Rather, the mineral was named after 19th-century Finnish geologist Victor Axel Hackman, a Finnish Geological Survey geologist and professor at the University of Helsinki.
Hackman joined fellow Finnish geologist and mineralogist Willhelm Ramsay for the Finnish Kola expedition that took place from 1891 to 1892. During the two men’s expedition, they recovered a rock called tawite in the Tavaiok river valley.
The rock was primarily composed of sulfur-bearing sodalite (hackmanite) and aegirine, leading to hackmanite’s first discovery and eventually, its first scientific description (from Ramsey) in 1898.
Since its discovery, hackmanite has been a vital material for scientific research, with studies on it dating as recently as 2021!
Scientific Discoveries from Hackmanite Research
Even before hackmanite’s official discovery, early-1800s geologists in Greenland had noticed that some bright pink sodalite specimens would quickly fade in color after being broken and exposed to sunlight, then eventually go back to their original color.
Moving into modern day, one important study on hackmanite occurred in 2020.
The 2020 study involved an international collaboration of scientists trying to uncover why certain hackmanites produce a strong fluorescence, or “afterglow,” to see how to create the most effective glow in synthetic hackmanite.
The scientists concluded that the best “afterglow” in hackmanite comes from a specific ratio of sulfur, potassium, titanium, and iron, with titanium glowing at the stone’s core.
Another significant study on hackmanite happened in 2022.
The 2022 study involved Finnish researchers studying how hackmanite reacts to nuclear radiation. They knew that hackmanite changed color from UV radiation X-rays, but they weren’t sure about how it’d react to other types of radiation.
Wait, is hackmanite radioactive? Nope, no need to worry about that.
The researchers discovered that hackmanite is radiochromic, meaning it changes color from exposure to alpha particles, beta particles, or gamma radiation.
Why is that important? Well, it means hackmanite can be used as an inexpensive, reusable, and non-toxic alternative for creating radiochromic films, which are used medically in radiology.
On the spiritual healing side, let’s look at hackmanite’s crystal healing benefits.
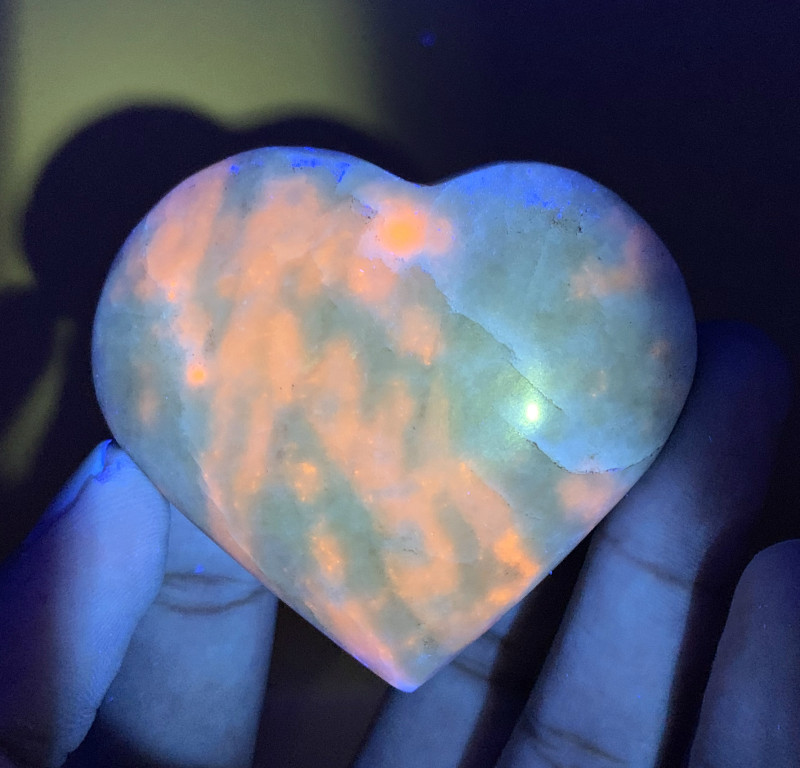

Hackmanite Healing Properties
Like all gems, hackmanite can be a healing stone. Pink hackmanite joins other pink gemstones in bringing self-love and acceptance. Blue hackmanite, like other blue gems, offers serenity and balance.
Purple to violet hackmanites are great crown chakra stones, balancing this energy center to help you ascend to the highest spiritual awareness.
Physical Healing
Outside of its potential use in radiology, some of the purported metaphysical hackmanite benefits include treating:
Insomnia
Night terrors
Reproductive health issues
Emotional Healing
Emotionally, hackmanite is said to help you self-reflect better. Crystal healers recommend using it to understand your true feelings and express them with confidence.
It’s also believed to improve your mental fortitude and willpower.
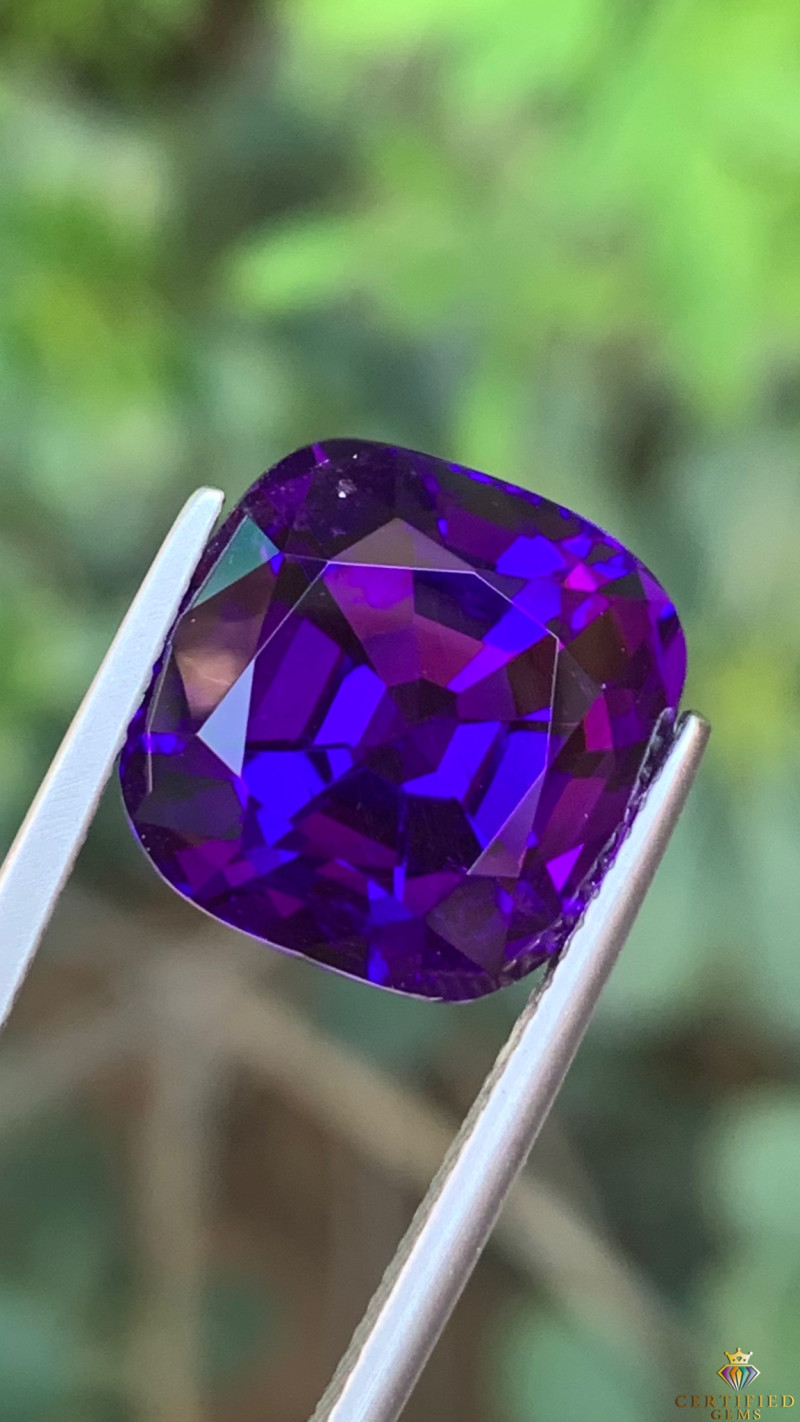

Hackmanite Gemstone Properties
As a gemstone, is hackmanite valuable? Its applications in medicine and rare glowing properties are certainly valuable, but its value as a gemstone depends on its color, cut, clarity, transparency, and sometimes source.
Color: Light pink to violet hackmanite is most common, so brighter pink or blue hackmanites are pricier. Color is less important as transparency and clarity.
Cut: Raw hackmanite is most affordable, while faceted hackmanites are rarest and usually most expensive. The most common cuts are hackmanite beads and cabochons.
Clarity: Some hackmanites have small black inclusions, and more visible inclusions mean significantly lower value.
Transparency: Transparent hackmanite crystals are rare and more valuable than translucent specimens, which are still more valuable than opaque ones.
Source: Transparent hackmanites from Afghanistan are generally the most expensive. However, hackmanites from the Mont Saint-Hilaire mine in Canada are nearly gone, making their specimens even pricier if good-quality.
Speaking of sources, how and where does hackmanite form?

Hackmanite Formation & Sources
Hackmanite forms like any sodalite mineral, but there must be sulfur present.
Sodalite minerals usually form inside igneous rocks that hardened from sodium-rich, silica-poor, and aluminum-poor magma. Some examples are nepheline syenite, phonolite, and trachyte.
Mining Locations
Where is hackmanite found? Currently, the top source for hackmanite gemstones is the original one: Greenland. Greenland’s hackmanites are often large, well-colored, and gem-quality with bright fluorescence.
Other notable hackmanite sources include:
Afghanistan
Canada
Guinea
Myanmar
Norway
Pakistan
Russia
USA (Arkansas, New Hampshire, New Jersey)
Afghanistan is notable for producing attractive pink hackmanites with creamy white fluorescence and long-lasting tenebrescence — many change to deep purple and stay that way for months if kept in complete darkness.

Hackmanite Gemstone Price & Value
Overall, hackmanite’s price per carat ranges from $5 to $2,500 per carat based on its appearance and source.
Opaque hackmanite beads or cabochons from Afghanistan, Greenland, or Myanmar are typically $5-$50 per carat. Transparent Afghanistan hackmanites of high-quality are often $500-$700 per carat.
Pure pink hackmanites from the near-depleted Mont Saint-Hilaire mines in Canada can be $2,000-$2,500 per carat.
Rough, transparent to translucent hackmanite crystals here at Gem Rock Auctions range from $0.40-$105 per carat. Our faceted hackmanite gemstones start around $40 and reach $150,000.
Hackmanite Care and Maintenance
Proper gemstone care for hackmanite is pretty easy. While the color can change in sunlight, it will always revert back. However, extreme heat can remove the tenebrescence, so keep that in mind.
Hackmanite has only mid-range hardness, so you may want protective settings on a hackmanite ring. Store hackmanite jewelry separately from other gemstones.
Clean hackmanite with a soft toothbrush, mild soap, and warm water.
Hypnotized by Hackmanite Yet?
At first glance, hackmanite may seem like an ordinary gem, but it's far from it. From its romantic hues to stunning color changes, hackmanite is a gem that belongs in every collection!
Search the Gemstone Encyclopedia
Related Auctions
Related Articles
Originally the Birthstones or gemstones were associated with a zodiac sign or the month of a individuals birth. Find out what your stone is and view the stones we have for sale
8th Feb 2021
There are dozens of quartz and chalcedony gems with various colors and patterns. Learn all about quartz properties and every type of quartz, from amethyst and agate to plasma and phantom quartz!
15th Oct 2020
Amber is an ancient fossilized tree resin, often with plants inside, that’s usually yellow-orange and dates back millenia. Learn the history, prices, and properties of amber!
8th May 2018
Latest Articles
Simpsonite is a lesser-known mineral known on the gem market for its durability, yellow-orange color, and rarity. Discover all the properties, uses, prices, and history of simpsonite.
3rd Mar 2025
Kurnakovite is a colorless crystal related to inderite and rarely faceted but known among collectors. Explore the mineral traits, history, prices, and more in this kurnakovite guide.
17th Feb 2025
Prosopite is an uncommon gemstone known for its rare robin’s egg blue form used for cabochons. Discover the history, benefits, prices, and powers of prosopite gemstones!
3rd Feb 2025
Article Categories
How To's is where you will find helpful articles from gem Rock Auctions on how to cut gemstones, select gemstones and buy gemstones.
9 Articles





