
Euclase Gemstone: Meaning, Healing Uses, Value & Information
 Euclase (yoo-klays) is a beryllium mineral famously from South America. It’s typically colorless or pale blue in the form of heavenly prismatic crystals. But is euclase a gemstone? You bet! Collectors often seek out these obscure gems.
Euclase (yoo-klays) is a beryllium mineral famously from South America. It’s typically colorless or pale blue in the form of heavenly prismatic crystals. But is euclase a gemstone? You bet! Collectors often seek out these obscure gems.
Obscure? Is euclase rare? Yes, euclase is a rare mineral and rarer gemstone. Large, facetable crystals are uncommon but exceptional to find. It’s also not widely known outside of gem enthusiast circles.
Interested in some enchanting euclase jewelry or crystals? Read on to get all the information on euclase gemstones, from their colors to their healing properties, prices, and more!
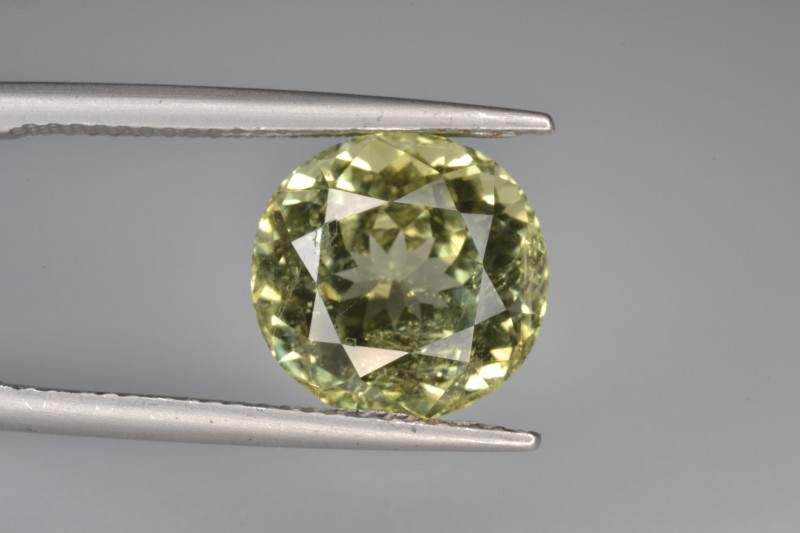
What Is A Euclase Gemstone?
Euclase is a semi-precious gemstone best known in the form of well-formed, baby blue to colorless crystals. It serves as a zodiac stone for Virgo and Sagittarius.
Color-zoned Colombian euclase can be mistaken for trapiche emerald. Euclase gems can also resemble aquamarine or white topaz. As such, euclase serves as an alternative March birthstone (for aquamarine) or April birthstone (for white topaz).
However, euclase is more expensive than aquamarine. Many sellers take advantage of this by labeling aquamarines as euclase to sell them for higher prices.
True euclase has a higher refractive index than aquamarine’s 1.57-1.58 RI. Plus, aquamarine’s density is lower at 2.75. You may confuse euclase with celestite as well, but celestite’s Mohs hardness ranking is much lower at 3-3.5.
Speaking of mineral properties, what is euclase made of?
Euclase Specifications & Characteristics
Euclase is a beryllium aluminum hydroxide silicate with the formula BeAISiO4(OH). It’s not a beryl variety, but it’s similar in composition, with beryl’s formula being Be3Al2Si6O18. Beryl is also involved in euclase’s formation but differs from euclase in crystal system and density.
Most euclase forms as distinctly prismatic and striated crystals. “Striated” means there are thin, parallel, slightly indented lines along the crystal’s flat sides (or “faces”). Typically, euclase striation occurs on the long sides, lengthwise.
The ends of euclase crystals may both be pointed (doubly-terminated) like a Herkimer diamond or have a chisel-like shape. Raw euclase may also form in fibrous or massive habits, along with (rarely) crystal clusters.
Here’s all the euclase mineral data:
Mohs hardness: 6.5-7.5 (may vary on different sides of same crystal)
Color: Colorless, white, light to dark blue, blue-green, light green, yellow-green, yellow, orange-pink, violet; May show color-zoning; Rarely mottled
Crystal structure: Monoclinic
Luster: Vitreous (glassy), slightly pearly on cleavages
Transparency: Transparent to translucent
Refractive index: 1.65-1.67
Density: 2.98-3.10; Zimbabwe crystals can be 3.06-3.13
Cleavage: Perfect 1-direction on [010] & good 2-direction on [110] and [001]
Fracture: Conchoidal
Streak: White
Luminescence: Sometimes weak fluorescence in deeper-colored material; Red in LW-UV & yellow in SW-UV
Pleochroism: Present, but colors vary by locality, crystal color, and impurities present; Pale crystals - blue-gray to light blue to colorless OR turquoise to yellow-green to colorless/pale green; Chromium-colored crystals - Turquoise to purple to colorless; Dark blue Zimbabwe crystals - strong in dark blue to sky blue to cyan; Pink crystals - pink to orange
Enough science, let’s learn about euclase’s spiritual meaning!

Euclase Meaning & History
Euclase symbolizes expression, self-awareness, and clarity, be it mental clarity or spiritual. It’s nicknamed the “Stone of Happiness.” White euclase specifically also represents receptivity, humility, and sincerity.
Etymology-wise, what does the name euclase mean?
The name “euclase” comes from two Greek terms: eu meaning “easily” and klasis meaning “fractured” or “broken.” This meaning reflects the crystal’s perfect cleavage that makes it particularly vulnerable to breaking apart.
History
The first euclase specimens discovered came from Brazil in 1785. French naturalist Joseph Dombey brought them back to Europe in 1785, where acclaimed French mineralogist René Just Haüy studied the new gem species.
Haüy was the first to describe (and name) euclase in his 1792 paper, Euclase. Observations on Physics, Natural History and the Arts (title translated from French).
That same year in 1792, reports appeared on euclase discovered near the Russian Ural Mountains near the Orenberg district. Nearly 200 years later in 1962, the Government Chemical Laboratories organization published findings of the first euclase in Australia.
Even as recently as 2016, a new color of euclase emerged. Miners in Brazil discovered a small amount of orange-pink euclase resembling Padparadscha sapphire in color. The stones hit the market in 2018, but supply depleted quickly.
Shifting from history to healing, what is euclase good for?
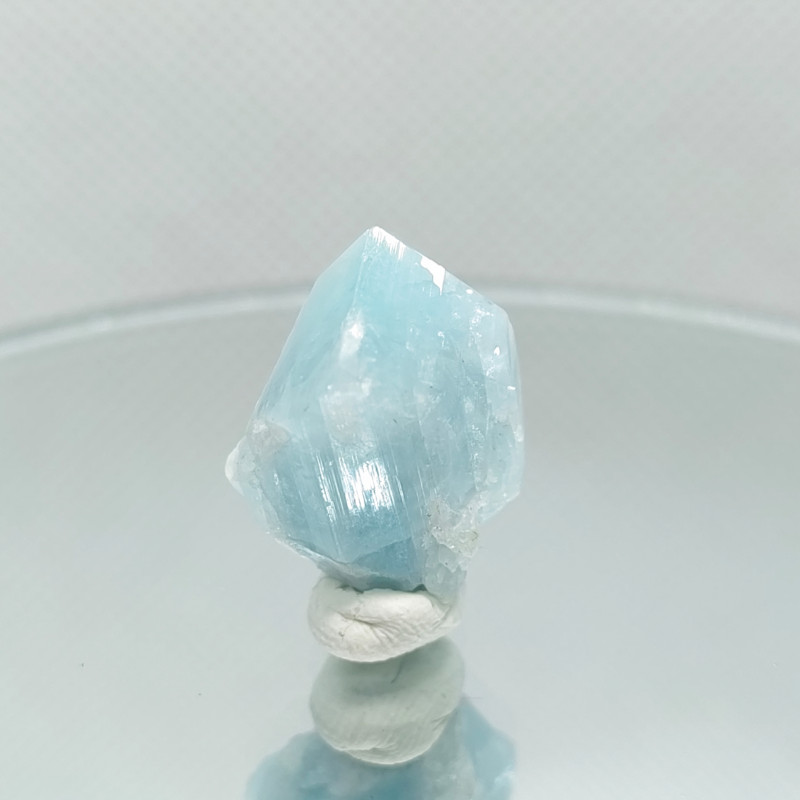

Euclase Healing Properties
Like all gemstones, euclase has various purported abilities as a healing stone. The specific healing powers can change based on euclase’s color.
When resembling aquamarine, euclase can possess the blue gemstone qualities of invoking calm, imparting wisdom, and inspiring honesty. Meanwhile, white euclase can raise spiritual awareness, purify spaces of negativity, and enhance meditation, like other white crystals.
Now, what is euclase used for in physical, emotional, and chakra healing?
Physical Healing
In crystal healing communities, popular physical euclase uses include:
Soothing pain or tension in muscles and joints
Cleansing bacteria from wounds
Suppressing muscle spasms
Enhancing vision
What about emotional uses?
Emotional Healing
The “Stone of Happiness” nickname comes from the belief that euclase encourages joy in creative pursuits, attracts luck, and of course, makes you happy!
Crystal healers praise the gem for helping its wearer quit unhealthy habits. They say the stone provides energy for you to replace those routines with positive ones more aligned with your goals.
Chakra Healing
Chakras are energy centers along your body that help different aspects of your mind, body, and spirit function their best. The chakras must be open to do this, and blockages prevent it. That’s where crystals come in!
Colorless euclase is a chakra stone for opening the third eye and crown chakras, allowing you to access your highest levels of spirituality. Blue euclase, on the other hand, opens the throat chakra, helping you speak your truth with confidence.

Euclase Gemstone Properties
The objective value of any euclase stone is predominated by its rarity. However, other factors to assess are color, cut, clarity, carat weight, and treatments.
Starting off, what color is euclase?
Color
Euclase used for gemstones is most often colorless, light blue, or light green. Crystals may also be yellow to green or have these colors as undertones (blue-green or yellow-green). A good amount from Zimbabwe is deep sapphire-blue.
Some blue stones have green speckling, while others have color-zoning in light to dark blue or colorless to blue hues. Not all euclase stones have patterns.
The cause of euclase color depends on the hue. Most stones get their coloring from varying amounts of iron impurities or transitions from ferrous iron (Fe2+) to ferric iron (Fe3+) or titanium (Ti4+).
Unusually vibrant greenish-blue euclase from Colombia is colored by chromium and/or vanadium. Orange-pink hues come from manganese (pink) and iron (orange) impurities.
Gems with high saturation carry high value. The rarest and most valuable color, however, is violet.
Cut
Euclase has good hardness, but its perfect cleavage makes faceting the stone difficult. Still, lapidarists (gem cutters) have achieved numerous faceted cuts with euclase, like emerald, marquise, and oval shapes.
Though colorless euclase may seem boring, it has great brilliance (light reflected from the interior) when cut well.
Unfaceted cuts like cabochons or carvings are less common.
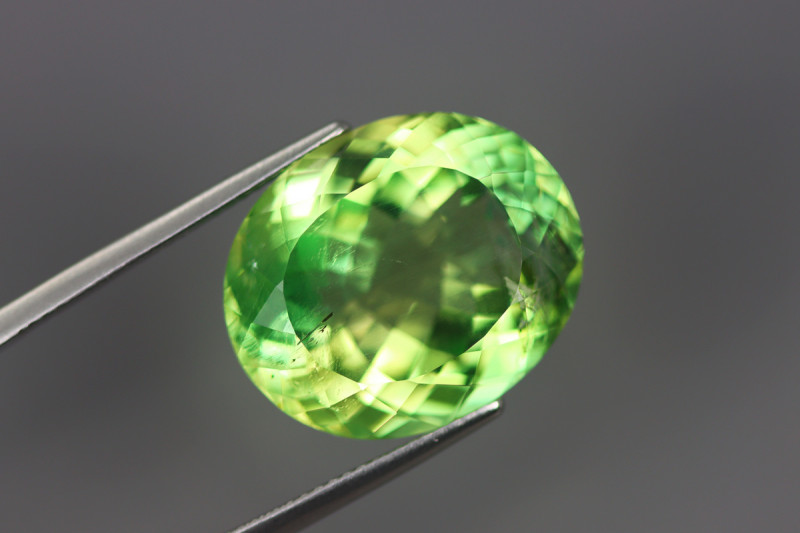
Clarity
Euclase clarity (the measure of a stone’s visible inclusions) is essential to determine if the stone is gem-quality. Stones with good clarity are rare and carry a high value.
Common inclusions in euclase are quartz and pyrite-like bravoite. Traces of impurities like iron and chromium can create color zoning.
Some blue-green Colombian euclase with color-zoning contains three-phase (fluid trapped in a cavity that splits into different phases) liquid, vapor, and halite inclusions. The main specimen, studied in 1996, also had high germanium impurities.
Transparent Brazilian euclase studied in 1980 showed peculiar inclusions of hematite plates, rutile needles, apatite crystals, and zircon grains.
Another colorless euclase from Brazil studied in 2021 showed needle-like crystals, suspended white to reddish-brown fibers, and brown fluid with a gas bubble inside a small, cylindrical cavity. Experts aren’t sure what the inclusions made of.
Carat Weight & Size
Almost all euclase crystals are small, with colorless ones typically only reaching 1 in (2.54 cm) long and 5-6 cts. However, some faceted, colorless euclase has been around 20 cts. Most green and blue euclase gemstones are 2-3 cts or lower.
Brazil and Colombia have produced unusually large euclase crystals. The largest euclase — a 144-carat, lime-green specimen held at the Smithsonian — came from Brazil. Gemstones made from rare violet euclase found in Brazil have reached 10 cts.
Treatments
Irradiation treatment is common for changing colorless euclase light green or blue.
Before people start cutting and treating it, how does euclase form in nature?
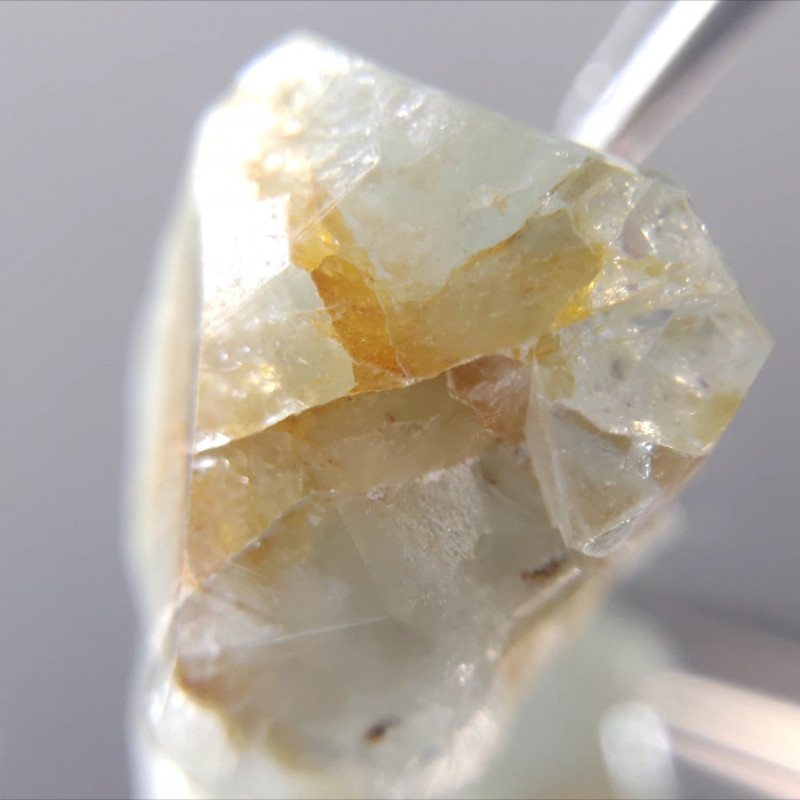

Euclase Formation & Sources
Most often, euclase forms in granite pegmatites when beryl minerals break down via hydrothermal replacement. Hot water containing other elements breaks down the beryl’s composition. The broken down elements reform into euclase as cooling happens.
In high (alpine) mountains, euclase forms similarly in hydrothermal veins, but at lower temperatures. Sometimes, the mineral forms in sedimentary mudrocks called black shales under medium temperatures. Fibrous or massive euclase forms in schists or phyllites (metamorphic rock that started as shale).
Geography-wise, where is euclase found?
Mining Locations
Brazil is the number-one source for gem-quality euclase, particularly with rare properties like pink or violet coloring, large size, or high birefringence. Colombia and Zimbabwe are also significant producers known for their vibrant euclase colors.
Additional sources for euclase crystals include:
Australia
Austrian Alps
China
Germany
Ireland
Myanmar
Norway
Russia
Tanzania
USA (Colorado)
Ready to browse euclase for sale? We’ll break down prices next!
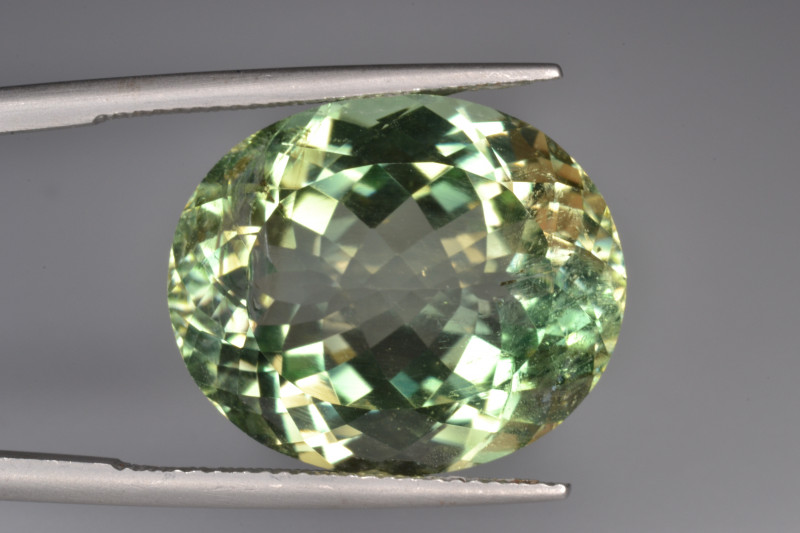
Euclase Stone Price & Value
Euclase’s rarity makes it among the priciest minerals. The most valuable gems have good clarity and intense green, blue, or violet coloring.
Wholesale faceted euclase price ranges (by color) are:
Light Blue: $10-$103 per carat, color-zoned gems can be $260-$360 per carat
Yellow-green: $35-150 per carat
Colorless: $100-$150 per carat
Green: $150-$450 per carat, highest-quality near $5,000 per carat
Yellow: $150-$580 per carat
Price ranges for rough euclase specimens at wholesale are:
Light blue: $5-$15 per carat, some reach $30 per carat
Colorless: $10-$15 per carat, flawless-clarity rough can reach $140 per carat
Bi-colored colorless & blue: $30-$60 per carat
Yellow: $3-$30 per carat
Jewelry-wise, colorless or light blue raw euclase pendants (without expensive metals) are generally $70 to $140 each. Zimbabwe’s darker blue raw euclase in pendants can be $1,200.
Colorless faceted gem rings cost around $700 per carat and blue faceted gem rings around $250 per carat.
Lastly, we’ll discuss gemstone care.
Euclase Care and Maintenance
When choosing jewelry, vulnerable options like a euclase ring should have protective settings. Avoid mechanical or steam cleaners. Only clean euclase with a soft brush dipped in a lukewarm water and mild detergent mixture. Store away from other gems.
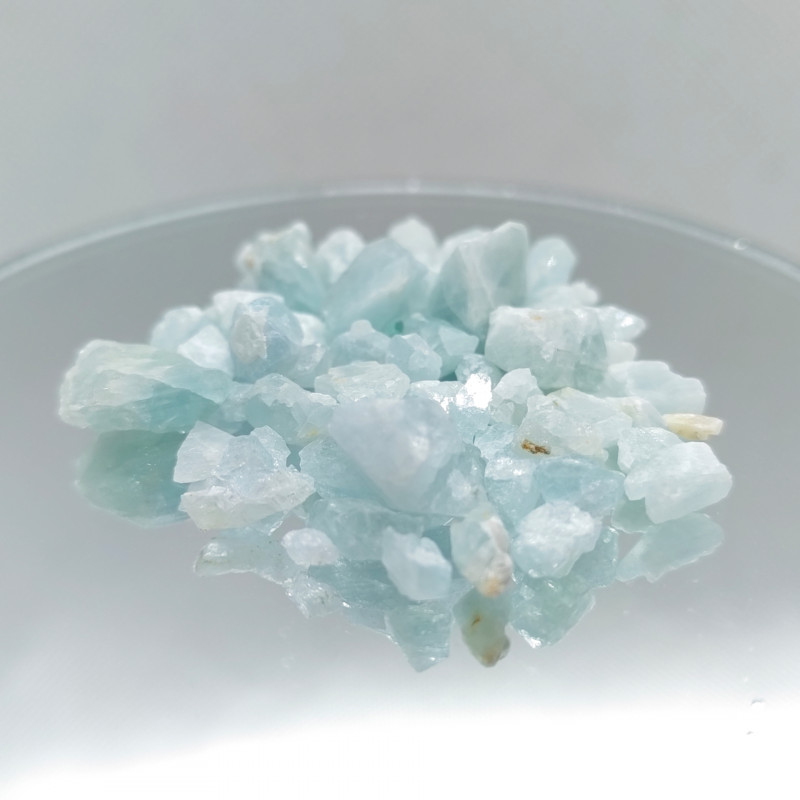

Want A “Happiness Stone” of Your Own?
Among gem collectors and crystal healers alike, euclase is a one-of-a-kind treasure with enigmatic properties. Its rarity will likely only increase with time, so there’s no better time to invest in this gem.
Whether you’re looking to embellish your space or seeking jewelry that emits optimism, euclase is a soft-hued yet powerful choice!
Search the Gemstone Encyclopedia
Related Auctions
Related Articles
Originally the Birthstones or gemstones were associated with a zodiac sign or the month of a individuals birth. Find out what your stone is and view the stones we have for sale
8th Feb 2021
There are dozens of quartz and chalcedony gems with various colors and patterns. Learn all about quartz properties and every type of quartz, from amethyst and agate to plasma and phantom quartz!
15th Oct 2020
Hackmanite is a pink to violet sodalite gem known for its unique color-change and luminescence. Learn why hackmanite is special, from its rare qualities to the types of hackmanite jewelry available.
28th Mar 2018
Latest Articles
Yugawaralite is a rare colorless, white, or pinkish zeolite crystal named for its discovery in Yugawara, Japan. Here we uncover the multifaceted history, properties, prices, and uses of yugawaralite.
24th Mar 2025
Simpsonite is a lesser-known mineral known on the gem market for its durability, yellow-orange color, and rarity. Discover all the properties, uses, prices, and history of simpsonite.
3rd Mar 2025
Kurnakovite is a colorless crystal related to inderite and rarely faceted but known among collectors. Explore the mineral traits, history, prices, and more in this kurnakovite guide.
17th Feb 2025
Article Categories
How To's is where you will find helpful articles from gem Rock Auctions on how to cut gemstones, select gemstones and buy gemstones.
9 Articles





